- Who is Building Polygon?
- What Problem is Polygon (MATIC) Solving?
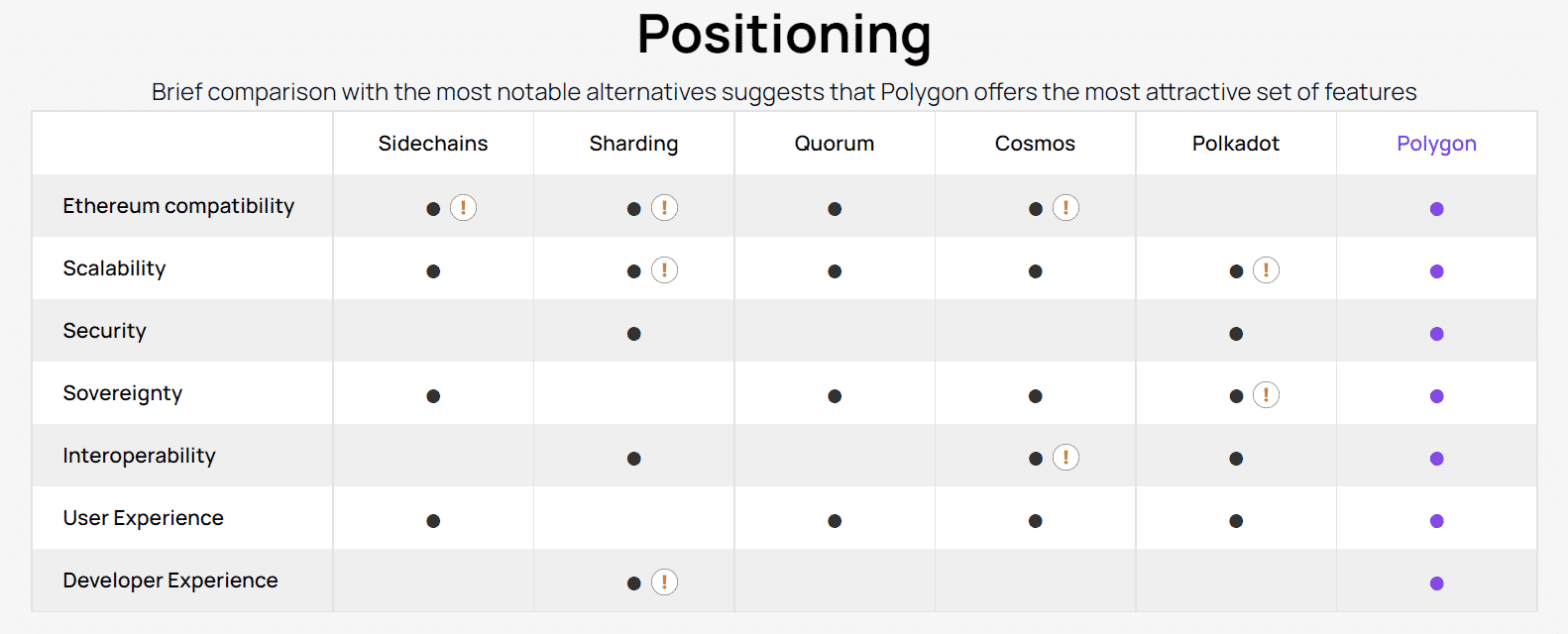
- How Does Polygon (MATIC) Work?
- Polygon’s $MATIC Token?
- Where Can You Buy Polygon’s $MATIC Token?
- Modest Overview of the Polygon Ecosystem
- Last Thoughts: Will Polygon “Fix” Ethereum?
Polygon (previously called Matic Network) is a layer 2 (L2) scaling service for Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks that makes it possible for quickly, economical, and safe off-chain deals for payments and basic interactions with off-chain clever agreements.
Polygon was at first released in 2017 under the name of Matic Network with the function of developing a procedure and a structure for structure and linking Ethereum-compatible blockchains utilizing a range of technical options.
Polygon’s existing flagship item is the Matic PoS Chain, an EVM-compatible sidechain protected by a permissionless set of PoS validators with a theoretical throughput capability of 65,000 transactions/second on a single Matic sidechain.
Polygon likewise developed a modular and extensible structure for developing Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks, composed in Golang, called Polygon SDK, and is additional dealing with 2 extra L2 scaling options, zk-Rollups and Optimistic rollups, based upon zero-knowledge and scams evidence respectively.
Who is Building Polygon?
The Polygon group has thirteen workers, with 4 technical co-founders, 6 extra designers, an item supervisor, and 2 marketing professionals. The core group is in addition supported by a neighborhood of trustworthy consultants, consisting of Hudson Jameson from the Ethereum Foundation, Ryan Sean Adams from Bankless, Anthony Sassano from EthHub & & SetProtocol, Pete Kim from Coinbase, and John Lilic– ex ConsenSys.
The core co-founding and advancement group includes CEO Jaynti Kanani, COO Sandeep Nailwal, CPO Anurag Arjun, and VP of engineering Mihailo Bjelic.
Jaynti Kanani is a full-stack designer and blockchain engineer who’s formerly added to lots of noteworthy tasks, consisting of Web3, Plasma, and WalletConnect.
Sandeep Nailwal is a blockchain developer, business owner, and co-founder & & CEO at ScopeWeaver, a company that offers blockchain items and seeking advice from services.
Anurag Arjun is a product/project supervisor who formerly worked for AVP, IRIS Business, Cognizant Technologies, and SNL Financial.
Mihailo Bjelic signed up with the Matic group as a co-founder and VP of engineering just recently, when the job rebranded to Polygon. Prior to signing up with Polygon, Bjelic dealt with comparable blockchain scaling options as Matic.
What Problem is Polygon (MATIC) Solving?
Polygon is dealing with Ethereum’s leading restrictions: scaling or deal throughput and bad user experience.
Instead of providing restricted scaling services like its predecessor Matic– which used an innovation referred to as Plasma that permits the development of personalized ‘kid’ blockchains to process deals off-chain prior to completing them on the primary Ethereum chain– Polygon is created to be an extensive procedure and structure for introducing interoperable blockchains.
Scaling is Ethereum’s earliest and most impeding issue. Ethereum’s existing deal throughput abilities are grossly inadequate to please the growing needs of the neighborhood. DeFi is exploding quick, and with the majority of it being developed on Ethereum, the procedure requires to scale the other day since the existing deal expenses are evaluating a huge bulk of the users.
When it pertains to scaling, blockchains can usually take 2 various courses:
- Scale the mainchain or the so-called layer one of the procedure, where tasks are normally required tо pick in between various compromises and make sure sacrifices in either decentralization, scalability, or security (aka the blockchain trilemma)
- Or, usage side chains that run on top of the mainchain (layer 2) to unload a few of the work and thus reduce the blockage on the primary chain.
In this regard, Ethereum’s method is to take both instructions at the same time– i.e., scale on layer one by carrying out sharding and transitioning to a proof-of-stake agreement system (Ethereum 2.0), and likewise utilize sidechain options like the one Polygon is developing to scale much more and faster.
Thanks to the Matic sidechain, the Ethereum network can scale considerably and do it successfully without making any sacrifices in regards to decentralization. Sidechains provide low-cost and practically instant deals that are eventually settled in batches on the mainchain, implying that they utilize the robust security of the mainchain without making any compromises in regards to efficiency.
How Does Polygon (MATIC) Work?
Polygon’s so-called Matic Sidechain works like any other PoS-based blockchain, with its own facilities, token, user nodes, validator nodes, native dapps, and so on, other than the deals are eventually batched and decided on the Ethereum mainchain (comparable to how Bitcoin’s L2 scaling option called Lightning Network works.)
You can think about the Matic sidechain as its own little interoperable community– part of the wider universe of Ethereum– using users exceptional efficiency and user experience. Every decentralized application developed on Ethereum or any other Ethereum-compatible blockchain can be ported to the Matic Sidechain and run there in a lot more performance-optimized environment.
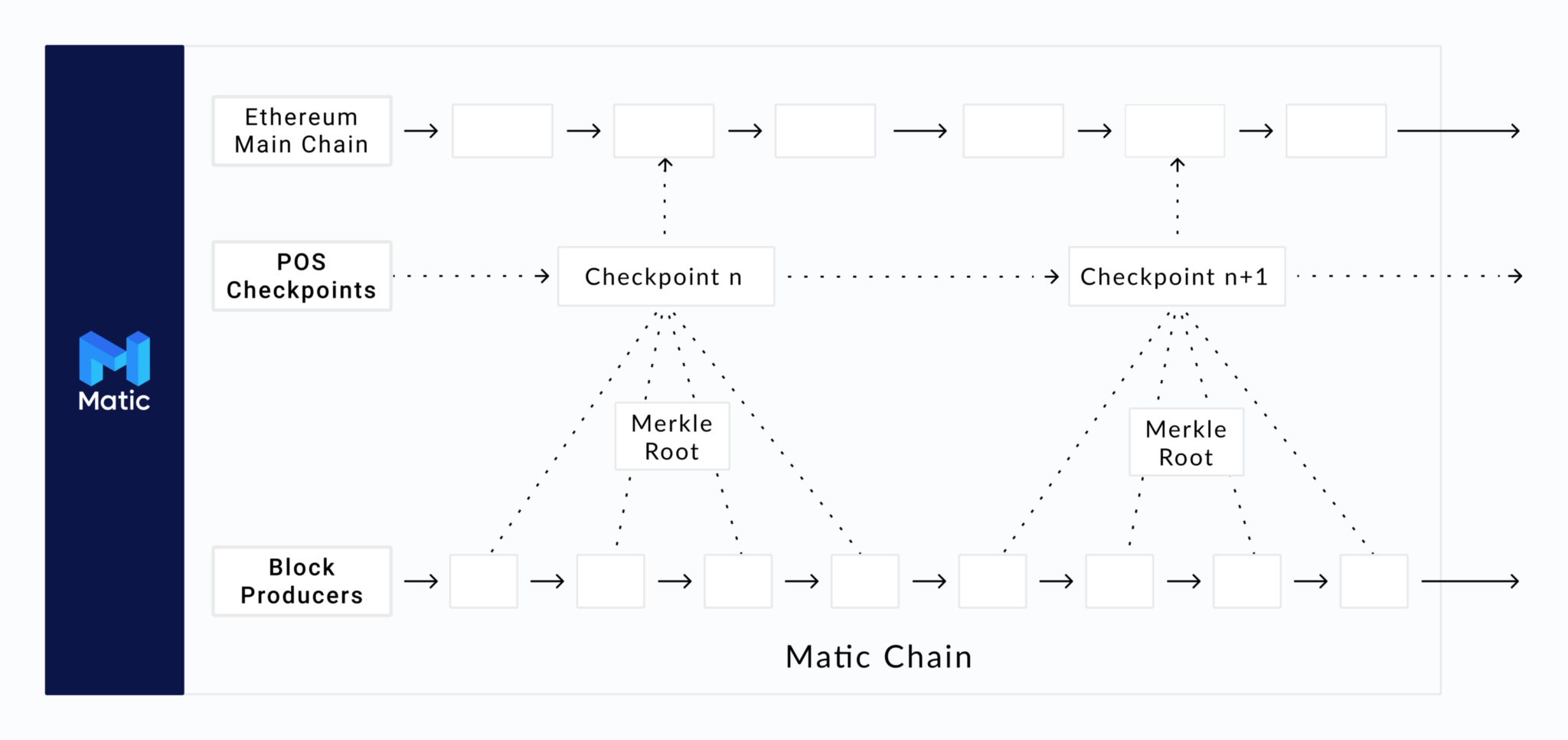
Users who want to connect with decentralized applications that have actually moved to the Matic Sidechain require to:
- Authorize the so-called Predicate Contract released on the Ethereum network, which locks the tokens to be released on the Matic Sidechain,
- When the Predicate Contract has actually been authorized; the next action is to transfer the tokens on the Matic Sidechain, which is done rather instantly. In this procedure, a specific clever agreement called RootChainManager sets off another clever agreement called ChildChainManager that mints the proper quantity of locked or transferred ERC20/ERC721/ERC1155 tokens on the Matic network.
- As soon as the user gets their tokens on the Matic Sidechain, they can move them practically instantly and with minimal costs within the network. This indicates that trading or offering liquidity utilizing a decentralized exchange such as SushiSwap on Matic will cost the user cents rather of $50-200, as holds true with utilizing the exact same procedure on the Ethereum mainchain.
- Withdrawing the tokens back to Ethereum is a two-step procedure: initially, the tokens need to be burnt on the Matic sidechain, and after that the evidence of this burn deal needs to be sent to the Ethereum mainchain. As soon as this procedure is finished (takes about 20-30 minutes), the RootChainManager wise agreement will immediately transfer back properties to the user’s address (wallet) back on the Ethereum mainchain.
Polygon’s $MATIC Token?
The MATIC token (ticker: MATIC) serves a range of functions within the Polygon community, consisting of spending for deal costs (comparable to how ETH tokens are utilized to spend for gas costs on the Ethereum mainchain), adding to security through staking, and taking part in the procedure’s decentralized governance by voting on Polygon Improvement Proposals (PIPs).
The present distributing supply of the MATIC token is 6.3 billion, while the overall token supply (difficult cap) is 10 billion. Users can likewise transform the MATIC token to other properties ported on the Matic Sidechain utilizing various token swap or exchange procedures on the network.
Where Can You Buy Polygon’s $MATIC Token?
Polygon is offered on popular cryptocurrency exchanges like Coinbase Pro BinanceFTX, and Huobi Global
Modest Overview of the Polygon Ecosystem
In basic, the Polygon environment includes numerous stars, consisting of users, designers, stakers, and block manufacturers.
Polygon users can utilize the Matic Sidechain to negotiate and engage with numerous Ethereum-based decentralized applications, much like they would do on Ethereum or any other blockchain, other than Matic is more affordable and quicker.
On the other hand, the designers are anticipated to utilize the Polygon Network and the Polygon SDK stack to develop their own sidechains or scale their own dapps to supply their users with an exceptional user experience.
The stakers on Polygon efficiently play the exact same function as PoW miners on Ethereum. They require to stake (lock) MATIC tokens to take part in confirming and validating deals on the Matic Sidechain. Utilizing their staked tokens as voting power, they can choose so-called block manufacturers (stakers that please particular requirements) to produce the blocks on the sidechain.
Block manufacturers are selected by the stakers to produce the blocks and eventually settle all deals on the network. They require to stake a substantial amount of MATIC tokens in order to certify and be chosen.
Usually, the variety of block manufacturers will be reasonably low since having less agreement developers permits greater throughput and much quicker deal settlements. The typical block time on the Ethereum mainchain is ~ 20 seconds, while the Matic Sidechain mines or develops and settles a brand-new block every second.
Last Thoughts: Will Polygon “Fix” Ethereum?
Possibly the critical element of Polygon’s worth proposal is that it is among the only layer-two scaling services constructed on Ethereum that has actually experienced moderate to mass adoption.
Polygon assists to substantially enhance Ethereum’s deal throughput and fix the high gas cost issue, however it likewise plays an essential function in enhancing the more comprehensive issue of blockchain interoperability.
Never Ever Miss Another Opportunity! Get hand chosen news & & information from our Crypto Experts so you can make informed, notified choices that straight impact your crypto earnings Register for CoinCentral totally free newsletter now.
